Azure Powershell
satya - 11/18/2019, 10:22:18 AM
Documentation: Getting started with azure powershell
satya - 11/18/2019, 10:33:21 AM
Few rules
1. command lets: ex: get-command, get-azvm, get-azFirewall
2. verb-noun
3. verb: actions: get, set, etc
4. noun: resource types: vms, data factories, databases
5. command lets are inside modules that get loaded
satya - 11/18/2019, 10:33:52 AM
Example
Get-Command -Verb Get -Noun AzVM* -Module Az.Compute
satya - 11/18/2019, 10:35:09 AM
Explanation
1. verb: get
2. noun: command
3. options: -verb, -noun, -module
4. module: az.compute
*May be they are case sensitive! don't know yet
satya - 11/18/2019, 10:36:44 AM
The module az.datafactory is documented here
satya - 11/18/2019, 10:42:54 AM
Working with managed identity through powershell for a data factory
Working with managed identity through powershell for a data factory
satya - 11/18/2019, 11:01:04 AM
Mastering azure cloud shell: article
satya - 11/18/2019, 11:24:04 AM
Some issues
1. When I invoked shell.azure.com it has created all the necessary assets like the storage account, resource group etc.
2. However it created it in a different location than I wanted.
3. i also don't know if this storage account is specific to a user or a group of users like at a subscription level!!
4. these are still things that need to be figured out
satya - 11/18/2019, 11:28:05 AM
How do you know what command lets are available
1. You search
2. how do you search? you use the following search commandlet
3. Get-command -verb get -noun *azdatafactory*
4. that will search for get commands whose name includes something to do with data factories
5. Then you can locate the documentation page for that commandlet. You can locate these command lets in the links provided in this document around azure powershell urls
satya - 11/18/2019, 11:30:43 AM
Here is another way to search the available commandlets
satya - 11/18/2019, 11:33:38 AM
Yet another way is
Go here first:
Then locate "Reference" on the left hand side to identify each module and commandlets with in that module and examples for each commandlet
satya - 11/18/2019, 12:07:19 PM
Few notes from that article
1. Azure Cloud Shell is assigned per unique user account and automatically authenticated with each session
2. You can always remove the Cloud Shell by deleting the Azure resource group, which you used during that setup process.
3. One of the great features of Cloud Shell is that you will find many tools already installed; one of them is SSH. If you want to connect to your VM directly from the Azure portal using SSH, you can fire up Cloud Shell and do so. This makes managing Linux much more comfortable. You can create and deploy and manage virtual machines directly from your web browser.
4. Looks like there is some sort of a cloud drive that is attached. Need to know more here.
5. It has an editor based on the Visual Studio Code open-source project Monaco
6. A PowerShell provider allows any data store to be exposed like a file system as if it were a mounted drive. In other words, the data in your data store can be treated like files and directories so that a user can navigate data via cd or dir. SHiPS is a PowerShell provider. To be more precise it?s a provider utility that simplifies developing PowerShell providers.
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:30:07 PM
Locating a datafactory by name
//This will locate a datafactory
$df = Get-AzDataFactoryV2
-ResourceGroupName "some-resource-group"
-Name "some-datafactory-1"
//Notice the V2 at the end of Get-AzDatafactorV2
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:30:28 PM
Use Get-AzDataFactoryV2 and not Get-AzDataFactory
Use Get-AzDataFactoryV2 and not Get-AzDataFactory
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:31:09 PM
You can do this also to find out names of these commands
Get-AzDataf
Now type tab to see the prompts
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:32:06 PM
You can do $df then to print out the nature of the data factory
> $df = ....some code that locates the data factory
> $df (this will print that object now)
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:32:40 PM
You can do this the methods and properties of that object
> $df.
//Notice the .
//Then press tab
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:33:13 PM
That will print the options as
DataFactoryId Identity
ProvisioningState ResourceGroupName
Equals GetType
DataFactoryName Location
RepoConfiguration Tags
GetHashCode ToString
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:35:28 PM
Some of these are properties and some are methods
Identity is a property
GetType is a method
So
1. $df.Identity
2. $df.GetType()
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:47:07 PM
Get the principal id first of the data factor
$df = Get-AzDataFactoryV2 -ResourceGroupname(name) -Name (datafactoryname)
$df.Identity
PrincipalId TenantId
----------- --------
2c97254a-a956-412a-8521-88bf61e6f956 e2ba767a-b27a-4f1d-b91a-309caf328df6
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:48:53 PM
Then you can get the managed identity like this
Get-AzADServicePrincipal -Objectid (principalid)
//You will get
ServicePrincipalNames : ....
ApplicationId : app-id-is-here
ObjectType : ServicePrincipal
DisplayName : factory-name
Id : principal-id
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:51:03 PM
Managed identity for a datafactory is supposed to show up here, but it doesn't
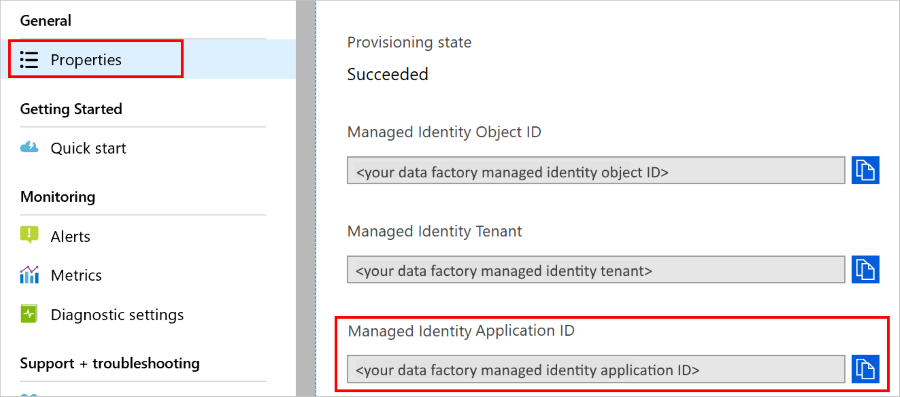
satya - 11/18/2019, 3:51:17 PM
thats why I had to jump the powershell hoops
thats why I had to jump the powershell hoops
satya - 11/28/2019, 11:17:46 AM
Azure automation and Powershell
satya - 11/28/2019, 11:38:38 AM
Powershell itself is documented here
satya - 11/28/2019, 12:42:03 PM
An exercise
//what is that command again with a Resource?
Az-GetCommand *azResource*
//ok I see it
Get-AzResource
//what kind of an object is an AzResource
//You can AzResource as a table with columns
Get-AzResource | Get-member
//Displays the members of Get-AzResource
//Explore the powershell core commands
Get-Command -module *core
Get-Module
Get-help
Get-command
etc.
//Expore utility commands
Get-Command -module *utility
Get-member is here in this module
satya - 11/28/2019, 12:44:49 PM
Lets look at a resource
//Get all resources
Get-azResource
//Take a resource id of one of them
$res = Get-azResource -ResourceId res-id
//Print it out
$res
/*
You will notice that not all
properties are printed
*/
//You can explicity print it
//for example
$res.properties
//you can then also do
$res.properties.state
//You can then tell if this resource
//is running or not
satya - 11/28/2019, 12:50:39 PM
here are the attributes of a resource object
Name MemberType
---- ----------
Equals Method
GetHashCode Method
GetType Method
ToString Method
ChangedTime Property
CreatedTime Property
ETag Property
ExtensionResourceName Property
ExtensionResourceType Property
Id Property
Identity Property
Kind Property
Location Property
ManagedBy Property
Name Property
ParentResource Property
Plan Property
Properties Property
ResourceGroupName Property
ResourceId Property
ResourceName Property
ResourceType Property
Sku Property
SubscriptionId Property
Tags Property
Type Property
satya - 11/28/2019, 12:51:05 PM
I have got this output from the command
Get-AzResource | Get-Member | Format-Table -Property name, membertype
satya - 11/28/2019, 12:52:29 PM
The format commands are in the utility module
Format-List
Format-Table
Format-Wide
Format-hex
Format-custom
satya - 11/28/2019, 12:56:07 PM
You can do this, hence
//This prints in a list format
Get-AzResource
//You can change that
Get-AzResource | Format-Table
satya - 11/28/2019, 1:00:27 PM
So, useful command so far
get-command
Get-Command -Verb Get -Noun AzVM* -Module Az.Compute
get-help
get-member
format-table
format-table -Propert some-prop-name
satya - 11/28/2019, 1:16:30 PM
where is a good command. do this
get-help where -examples
satya - 11/28/2019, 1:21:43 PM
where command
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Stopped"}
Get-Service | where Status -eq "Stopped"
Get-Process | Where-Object {$_.WorkingSet -GT 25000*1024}
Get-Process | Where-Object WorkingSet -GT (25000*1024)
Get-Process | Where-Object {$_.ProcessName -Match "^p.*"}
Get-Process | Where-Object ProcessName -Match "^p.*"
-------- Example 4: Use the comparison statement format --------
Get-Process | Where-Object -Property Handles -GE -Value 1000
Get-Process | where Handles -GE 1000
--------- Example 5: Get commands based on properties ---------
# Use Where-Object to get commands that have any
# value for the OutputType property of the command.
# This omits commands that do not have an OutputType
#property and those that have an OutputType property,
#but no property value.
Get-Command | where OutputType
Get-Command | where {$_.OutputType}
# Use Where-Object to get objects that are containers.
# This gets objects that have the
#**PSIsContainer** property with a value
# of $True and excludes all others.
Get-ChildItem | where PSIsContainer
Get-ChildItem | where {$_.PSIsContainer}
# Finally, use the Not operator (!) to
#get objects that are not containers.
# This gets objects that do have
#the **PSIsContainer** property and those
#that have a value of $False for the **PSIsContainer** property.
Get-ChildItem | where {!$_.PSIsContainer}
# You cannot use the Not operator (!) in the
#comparison statement format of the command.
Get-ChildItem | where PSIsContainer -eq $False
satya - 11/28/2019, 1:28:54 PM
Here is more documentation on working with objects
satya - 11/28/2019, 1:44:43 PM
see what it looks like
-eq is equal to 1 -eq 1
-ne Is not equal to 1 -ne 2
-lt Is less than 1 -lt 2
-le Is less than or equal to 1 -le 2
-gt Is greater than 2 -gt 1
-ge Is greater than or equal to 2 -ge 1
-like Is like (wildcard comparison for text) "file.doc" -like "f*.do?"
-notlike Is not like (wildcard comparison for text) "file.doc" -notlike "p*.doc"
-contains Contains 1,2,3 -contains 1
-notcontains Does not contain 1,2,3 -notcontains 4
satya - 11/28/2019, 1:50:30 PM
So I can do this
Get-AzResource | where {$_.name -like "*somename*"
satya - 11/28/2019, 2:07:57 PM
use this with caution
//Tell me what is running in my account
$resources = Get-AzResource
foreach ($res in $resources) {
$res1 = Get-AzResource -resourceid $res.resourceid
if ($res1.properties.state -eq "Running")
{
$res1.name + " is running"
}
}
satya - 11/29/2019, 3:23:20 PM
Azure Cloudshell is documented here
satya - 11/29/2019, 3:44:30 PM
where is the language reference for Microsoft Powershell?
where is the language reference for Microsoft Powershell?
Search for: where is the language reference for Microsoft Powershell?
satya - 11/29/2019, 3:45:01 PM
There is some discussion on that here: SOF
satya - 11/29/2019, 4:01:59 PM
Here is a link to one of those books: PDF
satya - 11/29/2019, 4:17:08 PM
what is $home in azure cloud shell?
what is $home in azure cloud shell?
satya - 11/29/2019, 5:08:07 PM
Here are key microsoft documents related to powershell
1. Azure powershell homepage is here
2. Azure powershell is documented here
3. Azure Cloud shell is documented here
4. very brief introduction to cloud shell editor
5. Equally brief introduction to cloud shell. . Especially missing is a detailed information about how the storage and file references work
satya - 11/29/2019, 5:14:38 PM
How to create a new file in azure cloud shell editor?
How to create a new file in azure cloud shell editor?
Search for: How to create a new file in azure cloud shell editor?
satya - 11/29/2019, 5:34:03 PM
So this editor looks like this
satya - 11/29/2019, 5:36:21 PM
You can start the code editor by also clicking on the icon for code
{}
satya - 11/29/2019, 5:38:01 PM
To see files that you create through the editor you have to do
The default shell has the root as
Azure:
However for file shares do
cd $home
This will put me somewhere like
PS /home/satya
You will see here the files created by code
- 11/29/2019, 5:39:04 PM
To create a new file
there is no icon or command
instead
On the command line
make sure you are in
PS /home/sayta>
now type
code some-new-file.ps1
This creates a new file and opens it
in the editor
annonymous - 11/29/2019, 5:40:44 PM
Azure cloud shell editor videos
Azure cloud shell editor videos
satya - 12/1/2019, 12:39:51 PM
Watching: Mastering Cloudshell: Thomas Maurer
satya - 12/1/2019, 12:40:50 PM
A good command: update-module powershell
A good command: update-module powershell
satya - 12/1/2019, 12:58:27 PM
Additional notes
1. it is a linux based container
2. Understand azure dashboard and use one from the start
3. what is a file share in azure? Because cloudshell uses one.
4. wonder what cd $home different from cd cloudrive
5. dir seem to give diff results in bash and powershell
6. what is clouddrive/scripts? what is in there?
7. He may have created them before. There are .ps1 files and .cli files in his example
8. cli: seem to be just javascript objects
9. root directory in powershell is azure:\>
10. You can pipe to more all outputs
11. Get-module show me modules loaded
12. get-module -ListAvailable will show available modules. a longer list
13. Find-module *visualstudio will show visual studio module in the much longer registry
14. then you can do install-module...
satya - 12/1/2019, 1:07:08 PM
More notes ...
1. cd $home is specific it seems to powershell
2. Not sure what $home here is.
3. Appears it is better to put files under the clouddrive directory
4. You can upload and download files from local drives through ui menus
5. Or use the Export-file commandlet
6. you can go to azure drive view by typing cd azure:. This is how you go there if you were to do cd $home and go to cloud drive.
7. Look into what Get-PSDrive is. Some kind of a provider. There are providers for file system, Azure, Environment, Function, Variables. Type Get-PSDrive to see this list
satya - 12/2/2019, 2:02:52 PM
Next set of notes
1. A cloudshell is really an entry point into a VM provided by azure. it creates a file share as well under a storage account using "file" as the storage type as opposed to blobs or a database. This storage is mounted on to the vm into a home directory and a sub directory called "clouddrive"
2. On this cloudshell vm not only can you see this "clouddrive" and other OS related directories (containing tools like git, java etc) but also a simulated directory tree under a drive called "azure:". This is provided by something calls SHiPS provider.
3. One can navigate azure: drive using a) dir b) cd ./some-.... c) tab to auto-fill long names in azure like subscriptions, resource groups, vms etc.
4. Get-Clouddrive is a command that tells the details of the mounted cloud drive
5. You can see the clouddrive as a directory in the azure portal under the "file" designation of the storage account. This file share then can be used to create new files or directories from the portal itself.
6. There appears to be an OS image in the storage account as well along with the tools that comprises the shell. (More research needed to speak more of this, but doesn't like such deeper knowledge is needed to understand the cloudshell.
7. In a way the "file" or file shares appear to be a similar kind of storage to "blobs" as a way to persist data. Of course there is difference.
satya - 12/2/2019, 2:29:24 PM
More notes...
1. Get_command gives details about a command. Looks like you can use comma separated list of these commands. An example
2. Get_command vi, emacs, nano, code: will provide commands that can invoke these commands from the command line of the shell
3. There is a plugin for VScode on your local machine. it is called "Azure Account". You can use this to "open." (via command pallette ctrl-shift-p) the azure cloud shell inside vscode without going to a browser. It is not clear yet if vscode so used will open files in local vscode (to be checked)
4. Get-Credentials is a commandlet that can be used to save userid/password credetials in a variable which can then be supplied to various other login commands as an input
satya - 12/2/2019, 2:44:00 PM
What is equivalent to Get-ComputerInfo in azure cloudshell?
What is equivalent to Get-ComputerInfo in azure cloudshell?
Search for: What is equivalent to Get-ComputerInfo in azure cloudshell?
satya - 12/2/2019, 2:45:31 PM
Few cloudshell demo scripts from Git hub location of Thomas Maurer
Few cloudshell demo scripts from Git hub location of Thomas Maurer
satya - 12/2/2019, 2:54:57 PM
What is ITOpsTalk.com
What is ITOpsTalk.com
satya - 12/2/2019, 2:57:09 PM
You can run powershell scripts from azure mobile portal as well.
You can run powershell scripts from azure mobile portal as well.
satya - 12/2/2019, 3:09:36 PM
Some powershell material from Pluralsight:John Savill
satya - 12/2/2019, 3:49:22 PM
can you mount azure cloud drive as a local drive windows?
can you mount azure cloud drive as a local drive windows?
Search for: can you mount azure cloud drive as a local drive windows?
satya - 12/2/2019, 4:03:46 PM
Documentation: How to use an azure file share on windows
satya - 12/2/2019, 4:08:30 PM
Useful AzureShell Commandlets
Get-command
Get-Command -Verb Get -Noun AzVM* -Module Az.Compute
Get-Command vi, nano, code, emacs
Get-help Get-command
Get-member
Get-AzResource | Get-member
Format-table
Format-table -Propert some-prop-name
Get-AzResource | Format-table ..options
Where
Where-Object
Get-AzResource | Where-Object....
Get-Module #installed modules
Get-Module -ListAvailable #Show all available ones
Find-Module
Install-Module
Export-file
Get-CloudDrive
Get-Credentials
#doesnt appear to be in CloudShell
Get-ComputerInfo
satya - 12/2/2019, 4:40:28 PM
How can I access or go to the file-share of the cloud shell in the portal?
1. Go to shell.azure.com
2. Locate the icon at the top for upload/download files
3. click on it
4. you will see a drop down
5. there is an item called "Manage file share"
6. that menu option will take you to the file share location in the portal in a separate browser window
satya - 12/2/2019, 5:38:11 PM
Documentation: How to debug azure file share problems
satya - 12/3/2019, 10:34:15 AM
command let for powershell version
command let for powershell version
satya - 12/3/2019, 10:35:07 AM
here is a discussion on SOF on this
satya - 12/3/2019, 10:36:28 AM
Short answer
1. It is not a commandlet to get the version
2. Instead, apparently there are built in variables
3. $PSVersionTable will print the version
4. To know what variables are available use the commandlet Get-Variable
satya - 12/3/2019, 10:41:02 AM
Here is the output of Get-variable
args
ConfirmPreference
ConsoleFileName
DebugPreference
Error
ErrorActionPreference
ErrorView
ExecutionContext
false
FormatEnumerationLimit
HOME
Host
InformationPreference
input
MaximumAliasCount
MaximumDriveCount
MaximumErrorCount
MaximumFunctionCount
MaximumHistoryCount
MaximumVariableCount
MyInvocation
NestedPromptLevel
null
OutputEncoding
PID
PROFILE
ProgressPreference
PSBoundParameters
PSCommandPath
PSCulture
PSDefaultParameterValues
PSEdition
PSEmailServer
PSHOME
PSScriptRoot
PSSessionApplicationName
PSSessionConfigurationName
PSSessionOption
PSUICulture
PSVersionTable
PWD
ShellId
StackTrace
true
VerbosePreference
WarningPreference
WhatIfPreference
satya - 12/3/2019, 10:46:44 AM
Get-Alias: Similarly you can find out about various aliases
#Show all aliases
Get-Alias
#Show aliases starting with letter g
Get-Alias g*
satya - 12/3/2019, 10:48:50 AM
Default modules loaded on windows powershell
Get-Module | Format-Table -property name
Microsoft.PowerShell.Management
Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility
PSReadline
satya - 12/3/2019, 10:53:39 AM
Here is how to install azure powershell module
satya - 12/3/2019, 11:50:12 AM
Using Get-Help better
To see the examples, type: "get-help Set-AzContext -examples".
For more information, type: "get-help Set-AzContext -detailed".
For technical information, type: "get-help Set-AzContext -full".
For online help, type: "get-help Set-AzContext -online"
satya - 12/3/2019, 11:50:46 AM
How to see current subscription in azure powershell
How to see current subscription in azure powershell
Search for: How to see current subscription in azure powershell
satya - 12/3/2019, 11:56:01 AM
The path to these commandlets
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us
/powershell
/module
/az.accounts
/get-azcontext
satya - 12/3/2019, 11:56:32 AM
Az.Accounts is an important module
Az.Accounts is an important module
satya - 12/3/2019, 12:09:57 PM
Choosing a subscription to work with in powershell
#Login
Connect-AzAccount
#Get a list of valid subscriptions
Get-AzSubscription
#See what is your current subscription
Get-AzContext
#Change to the desired subscription
Set-AzSubscription -subscription "sub-name"
#See the current subscription again
Get-AzContext
satya - 12/3/2019, 1:27:20 PM
Running a .ps1 file
//locate your directory
cd some-dir
//see files
dir test1.ps
//run it. This will not work
test1.ps
//but this will
./test1.ps
satya - 12/3/2019, 2:12:30 PM
A .ps1 utility to debug file shares
satya - 12/3/2019, 3:50:48 PM
Here is the command used to install Powershell azure modules
Install-Module -Name Az -AllowClobber -Scope AllUsers
satya - 12/3/2019, 3:51:46 PM
After the install the module list now is
Az.Accounts
Az.Billing
Az.Storage
CimCmdlets
DnsClient
Microsoft.PowerShell.Management
Microsoft.PowerShell.Security
Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility
Microsoft.WSMan.Management
NetAdapter
NetSecurity
NetTCPIP
PackageManagement
PowerShellGet
PSReadline
SmbShare
satya - 12/3/2019, 4:18:45 PM
Using Git in cloudshell via personal access token is first mentioned here
Using Git in cloudshell via personal access token is first mentioned here
satya - 12/3/2019, 4:19:01 PM
Using Git credentials in Azure cloudshell
Using Git credentials in Azure cloudshell
satya - 12/3/2019, 5:38:07 PM
How to enter command with password for git pull?
satya - 12/4/2019, 5:22:58 PM
String processing in Powershell
String processing in Powershell
satya - 12/4/2019, 5:23:54 PM
Microsoft Devblogs: Variable expansion in strings and here-strings
Microsoft Devblogs: Variable expansion in strings and here-strings
satya - 12/5/2019, 10:40:15 AM
Concepts/Learning path for Azure Powershell
satya - 12/5/2019, 10:41:54 AM
:) Just one small piece in a bigger picture
satya - 12/5/2019, 11:50:55 AM
windows powershell is documented here (not azure)
satya - 12/5/2019, 11:57:23 AM
writing functions is documented here
satya - 12/5/2019, 1:46:17 PM
Article: The Complete Guide to PowerShell Punctuation
satya - 12/5/2019, 1:54:04 PM
calling functions through Grouping Expression in powershell
calling functions through Grouping Expression in powershell
Search for: calling functions through Grouping Expression in powershell
satya - 12/5/2019, 1:56:41 PM
Example
#wrong
"Some string" + somefunc("hello")
#still wrong
"Some string" + somefunc "hello"
#still wrong
"Some string $(somefunc("hello")"
#Good: Group the func
"Some string" + (somefunc "hello")
#Good: Or another grouping
"Some string $(somefunc "hello")"
satya - 12/5/2019, 2:39:35 PM
Reading an environment variable
function getEnvVariable($name)
{
#Do this silently -ErrorAction ignore
$value = Get-ChildItem -Path "Env:$name" -ErrorAction Ignore
return $value
}
satya - 12/5/2019, 2:40:08 PM
How to call a commandlet to ignore intermediate error messages?
use the -ErrorAction Ignore
satya - 12/5/2019, 3:14:52 PM
Set environment variable
function setEnvVariaable ($name, $value)
{
Set-Item -Path "Env:$name" -Value $value -ErrorAction Ignore
}
satya - 12/5/2019, 3:16:03 PM
Using Write-Host as a print statement
function main {
$what = Read-Host -Prompt "What command: reset, show, set, otherwise"
if ($what -eq "reset")
{
Write-Host "Resetting token"
resetAccessToken
return
}
elseif ($what -eq "show")
{
Write-Host "Showing the Access token that is in the enviornment"
showAccessToken
return
}
elseif ($what -eq "set")
{
Write-Host "Prompt and set the variable"
clone
return
}
Write-Host "Default. Nothing to be done"
}
satya - 12/5/2019, 3:17:04 PM
Beware the behavior of implicit returns in powershell functions
Beware the behavior of implicit returns in powershell functions
Search for: Beware the behavior of implicit returns in powershell functions
satya - 12/5/2019, 8:08:38 PM
You can help vscode by type hinting variables
#Call a function that returns a string
#normally....
$curDir = getCurDir
#You can do this instead
#as needed
[String]$curDir = getCurDir
#Then vscode will tell you
#the properties and functions of String class
#Example
$curDir.
satya - 12/5/2019, 9:00:57 PM
Here is sample code article I posted on linkedin
satya - 12/7/2019, 7:09:12 PM
Helping vscode with type hints
#Get an element from an ordered dictionary
function getADirectory ($seq) {
[System.Collections.Hashtable]$d = $dirDictionary;
[System.Collections.ICollection]$list = $d.Keys
[string[]]$keyList = @($list.GetEnumerator())
$keyList.Get($seq)
}
satya - 12/7/2019, 7:12:00 PM
Because we use hash tables, arrays, and strings so often
We use hashtables, arrays and strings often in powershell script
It is good to know their types
This helps vscode to tell what methods are available on these variables
Especially the first time users
You can declutter the code later
These are useful not for maintenance but for first time coding
Once you are well vesed, you will remember the methods
For the reader that comes later, it is not necessary to know the types but just the method names. this is one way to navigate between typed and typeless environments
satya - 12/7/2019, 7:14:51 PM
How do I know the types?
Sometime using commandlet | Get-Member will tell you
But it is not possible all the time
Look up the powershell language reference to see the type used
Typically this type looks like "System.Collections..Hashtable"
If the vscode won't tell you the type returned by say "GetEnumerator", just google that type name and that will point to a C# class reference in .net at microsoft. Now you can tell the types returned
Plug that type name in vscode editor. now the editor will tell you the methods that you can cross check from web reference
satya - 12/9/2019, 11:26:12 AM
Measure-Object: Counting things in Powershell: Sum, Product, Average etc
#Count number of aliases
alias | Measure-Object
alias | Measure-Object -Property name
satya - 12/9/2019, 11:27:11 AM
Language reference for module powershell.utility
satya - 12/9/2019, 11:49:57 AM
Few hints
#Investigate the object type of an alias
#Why retrieve all aliases? Just get a few
alias | Select-Object -First 5 | get-member
