Gilbert Strang and Linear Alzebra
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:13:40 PM
Strang's Vectors: A Poem
Two vectors lie in a plane Each at a varied incline As they dance together There isn't a square That is uncovered in the infinite plane
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:14:04 PM
Explanation
When two vectors are added with different weights in a plane the resultant vecctor can take any point on that plane.
The visual geometric proof is very simple and elegant.
U keep one vector constant and change the size of the other vector from negative infinity to positive infinity.
That traverses a line. Now the other vector can move the line from one end to the other covering all space.
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:15:39 PM
AX: is a way to linearly combine all columns into a resulting column
AX: is a way to linearly combine all columns into a resulting column
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:16:37 PM
XA: is a way to linearly combine all rows of A into a resulting row
X is a row of weigths.
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:21:38 PM
Topics we are expected to know
Column Vectors
Row vectors
Elimination Matrices
Sub Spaces
Least Squares
Determinants
Inverses
Pivots
Singular
Eigen Values
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:21:50 PM
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors are an astonishing way to understand a square matrix - GS
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors are an astonishing way to understand a square matrix - GS
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:22:55 PM
And the Fast Fourier Transform (multiplying quickly by F and F-1) is a revolutionary algorithm. - GS
And the Fast Fourier Transform (multiplying quickly by F and F-1) is a revolutionary algorithm. - GS
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:24:15 PM
The truth is that vectors and matrices have become the language to know - GS
Calculus is mostly about one special operation (the derivative) and its inverse (the integral). Of course I admit that calculus could be important .... But so many applications of mathematics are discrete rather than continuous, digital rather than analog. The century of data has begun! You will find a light-hearted essay called "Too Much Calculus" on my website. The truth is that vectors and matrices have become the language to know.
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:25:43 PM
A key goal is learning to "read" a matrix - GS
A key goal is learning to "read" a matrix. You need to see the meaning in the numbers. This is really the essence of mathematics-patterns and their meaning.
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:26:25 PM
The greatest encouragement of all is the feeling that you are doing something worthwhile with your life - GS
The greatest encouragement of all is the feeling that you are doing something worthwhile with your life - GS
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:27:22 PM
The heart of linear algebra is in two operations-both with vectors - GS
The heart of linear algebra is in two operations-both with vectors - GS
satya - 1/5/2018, 5:28:39 PM
x-y coordinate system
The entire x-y plane and every point on that place can be seen as a linear collection vectors on the X and the Y axis
satya - 1/5/2018, 6:01:15 PM
what does a dot product of 2 vectors truly represent?
what does a dot product of 2 vectors truly represent?
Search for: what does a dot product of 2 vectors truly represent?
satya - 1/5/2018, 6:06:41 PM
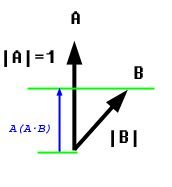
Best way to understand is this
A.B = |A|.|B|.cos(angle)
Or
A.B = |A|.[|B|.cos(angle)]
that means
project vector B on to vector A and see what is its length. Then multiply the length of A with it. This means the magnitude of B is reduced by its angle and then see what their multiplier of the new adjusted magnitudes are.
satya - 1/5/2018, 6:08:02 PM
Best explanation
satya - 1/5/2018, 6:08:28 PM
Taken from: https://www.mvps.org/directx/articles/math/dot/index.htm
satya - 1/5/2018, 6:08:56 PM
Project it first and then multiply with the other length
Project it first and then multiply with the other length
satya - 1/5/2018, 6:10:32 PM
Better yet: http://math.oregonstate.edu/bridge/papers/dot+cross.pdf
Better yet: http://math.oregonstate.edu/bridge/papers/dot+cross.pdf
satya - 1/5/2018, 6:22:44 PM
I like what it says and how I remember from my engineering days
it is fundamentally a projection
satya - 1/5/2018, 7:39:31 PM
Pivots in elimination cannot be zero
Pivots in elimination cannot be zero
satya - 1/5/2018, 7:40:13 PM
U - Upper Triangular, whole purpose of elimination
The matrix left behind after eliminating all variables except the last one.
satya - 1/5/2018, 7:40:35 PM
A determinant is the multiplication of all pivots of the U matrix
A determinant is the multiplication of all pivots of the U matrix
satya - 1/5/2018, 7:41:32 PM
Most of the elimination in linear equations is SQL like operations on row vectors, or rows
Most of the elimination in linear equations is SQL like operations on row vectors, or rows
satya - 1/5/2018, 8:00:28 PM
Element (3,4) of a resulting matrix
multiple row 3 with column 4 of the respective multiplying matrices :)
satya - 1/5/2018, 8:02:34 PM
Each elimination step is done by a separate elimination matrix
Each elimination step is done by a separate elimination matrix
satya - 1/5/2018, 8:03:48 PM
In the end multiply all elimination matrices to get a single elimination matrix: E E A = U
where U is the upper triangular
satya - 1/5/2018, 8:05:34 PM
Fun part is the big E matrix above tells us the whole story in a single matrix: That ought to be NICE
Fun part is the big E matrix above tells us the whole story in a single matrix: That ought to be NICE
satya - 1/5/2018, 8:07:36 PM
A permutation matrix swaps two rows of a matrix
A permutation matrix swaps two rows of a matrix
satya - 1/5/2018, 8:08:37 PM
Kind of the flipped identity matrix on the left
Kind of the flipped identity matrix on the left
satya - 1/5/2018, 8:44:12 PM
Beautiful: Every column of a right side matrix produce an independent column that is a combination of left hand side matrix columns
Beautiful: Every column of a right side matrix produce an independent column that is a combination of left hand side matrix columns
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:11:06 PM
A permutation matrix exchanges rows of a matrix
A permutation matrix exchanges rows of a matrix
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:11:26 PM
A permutation matrix is an identity matrix with its rows exchanged
A permutation matrix is an identity matrix with its rows exchanged
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:13:12 PM
PA=LU: The generalized elimination matrix formula
P - The permutation matrix
A - The augmented matrix of linear equations
L - The lower triangle matrix via elimination
U - The upper triangular matrix of what is left
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:15:23 PM
Permutation matrix is an identity matrix with reordered rows - GS
Permutation matrix is an identity matrix with reordered rows - GS
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:16:39 PM
There are n! ways of reordering rows in a matrix
There are n! ways of reordering rows in a matrix
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:19:48 PM
Inverse of a P is the same as its transpose
P(-1) = P(T)
P Inverse = P Transposed.
In other words if you want to find an inverse of a permutation matrix P, just transpose it.
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:20:18 PM
P.P(T) = I as in P.P(-1) = I
P.P(T) = I as in P.P(-1) = I
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:21:41 PM
Symmetric matrix is one when transposed it yields the same
A is symmetric if
A = A(T)
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:23:21 PM
R.R(T) is always symmetric
[R.R(T)](T) = [R(T)(T).R(T)]
= [R.R(T)]
See we ended up with the same
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:42:56 PM
So what is a vector space
where a set of vectors when combined linearly (add, subtract, multiply) still stay in the same selected space.
So an XY plane is a vector space.
A quadrant is not a vector space because a combination of two vectors will yield vectors outside of that.
Any line that goes through the origin is a vector space because the vectors on that line can dance together and never cross that line :)
However a line that doesn't go through the origin will shoot that line above or below based on a multiplier and thus escaping the original space where the vector came from
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:46:55 PM
Spaces in R2:
1, Entire plane
2. Any line through zero
3. The origin itself
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:47:29 PM
A line in R2 is not R1 because it has 2 components while R1 has only 1 component
A line in R2 is not R1 because it has 2 components while R1 has only 1 component
satya - 1/14/2018, 11:55:26 PM
How do you create a subspace from a matrix?
Take its columns
Consider each column a vector
And the column space will come from all linear combinations of those vectors. All linear combinations mind you!!
